Valid 70-341 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 70-341 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 70-341 VCE dumps and 70-341 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 70-341 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 70-341 dumps with VCE and PDF here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 70-341 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM
QUESTION 81
Your company has offices in Miami, Singapore and Montreal. An Active Directory site exists for each office. You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains a server in each site. Each server has the Mailbox server role and the Client Access Server role installed. All users connect to the Miami servers to retrieve the public folder hierarchy. You need to create several public folders on the server in the Singapore office to meet the following requirements:
– Ensure that the public folders are available if a single Mailbox server fails.
– Ensure that the users in the Singapore office connect to their local server to retrieve the public folder hierarchy.
Which actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose all that apply.)
A. Create a new public folder mailbox.
B. Create a new public folder database.
C. Run the Add-MailboxDatabaseCopy cmdlet.
D. For each mailbox in the Singapore office, run the Set-Mailbox cmdlet and specify the-defaultpublicfoldermailbox parameter.
E. Run the Set-PublicFolderDatabase cmdlet.
F. For each public folder mailbox, run the Set-Mailbox cmdlet and specify the-defaultpublicfoldermailbox parameter.
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
Public Folders.
Public folders can also be used as an archiving method for distribution groups. When you mail- enable a public folder and add it as a member of the distribution group, email sent to the group is automatically added to the public folder for later reference. Public folders are designed for shared access and provide an easy and effective way to collect, organize, and share information with other people in your workgroup or organization. Public folders help organize content in a deep hierarchy that’s easy to browse. Users will see the full hierarchy in Outlook, which makes it easy for them to browse for the content they’re interested in.
Public folder architecture.
In Exchange 2013, public folders were re-engineered using mailbox infrastructure to take advantage of the existing high availability and storage technologies of the mailbox database. Public folder architecture uses specially designed mailboxes to store both the public folder hierarchy and the content. This also means that there’s no longer a public folder database. High availability for the public folder mailboxes is provided by a database availability group (DAG).
NOT B
In Exchange 2013, public folders were re-engineered using mailbox infrastructure to take advantage of the existing high availability and storage technologies of the mailbox database. Public folder architecture uses specially designed mailboxes to store both the public folder hierarchy and the content. This also means that there’s no longer a public folder database. There is no database-level setting in Exchange 2013. Exchange 2013 has a mailbox-level ability to specify the public folder mailbox, but by default Exchange auto-calculates the per-user hierarchy mailbox.
NOT E
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997225(v=exchg.141).aspx
Use the Set-PublicFolderDatabase cmdlet to set attributes of public folder databases (Exchange Server 2010). There’s no longer a public folder database in Exchange Server 2013. There is no database-level setting in Exchange 2013. Exchange 2013 has a mailbox-level ability to specify the public folder mailbox, but by default Exchange auto-calculates the per-user hierarchy mailbox.
NOT F
Need to set it in the Singapore Office. Miami users still use the Miami servers to connect to the public folder hiearchy.
A
Need to create a public folder mailbox in the Singapore office. Public folder architecture uses specially designed mailboxes to store both the public folder hierarchy and the content. This also means that there’s no longer a public folder database.
C
Use the Add-MailboxDatabaseCopy cmdlet to create a passive copy of an existing active mailbox database. The specified Mailbox server must be in the same database availability group (DAG), and the DAG must have quorum and be healthy.
D
Use the Set-MailboxServer cmdlet to modify attributes on a computer running Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 with the Mailbox server role installed. In Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010, you could specify which users had access to specific public folders. In Exchange 2013, you can set the default public folder mailbox per user. To do so, run the Set-Mailbox cmdlet with the DefaultPublicFolderMailbox parameter. This ensures that the users in the Singapore office connect to their local server to retrieve the public folder hierarchy.
QUESTION 82
Drag and Drop Question
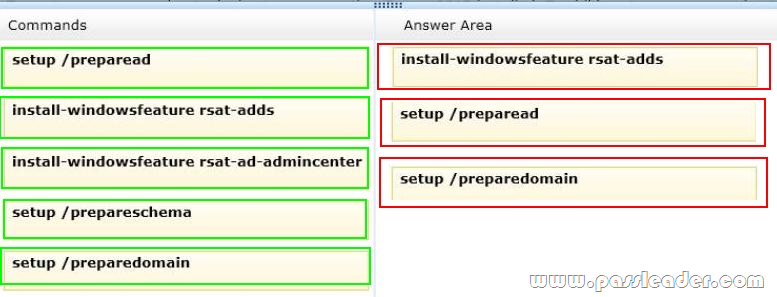
Your company plans to deploy an Exchange Server 2013 organization. The network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains two domains named contoso.com and child.contoso.com. The forest contains one Active Directory site. To contoso.com, you plan to deploy two servers that have Exchange Server 2013 installed. To child.contoso.com, you plan to deploy two servers that have Exchange Server 2013 installed. To the contoso.com domain, you deploy a new member server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012. You need to prepare the forest for the planned deployment of Exchange Server 2013. Which three commands should you run from Server1? To answer, move the three appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

QUESTION 83
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You need to ensure that an administrator named Admin1 receives a daily email message that contains a log of all the Exchange Server administrative actions. Which cmdlet should you use in a scheduled task?
A. Set-AdminAuditLogConfig
B. Write-AdminAuditLog
C. New-AdminAuditLogSearch
D. Search-AdminAuditLog
Answer: C
Explanation:
New-AdminAuditLogSearch: Exchange 2013 Help
QUESTION 84
Drag and Drop Question
Your network contains four servers. The servers are configured as shown in the following table.
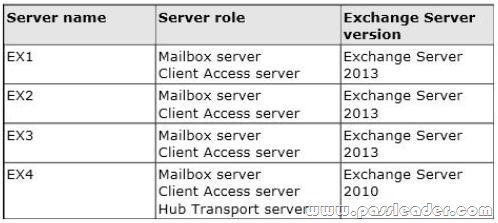
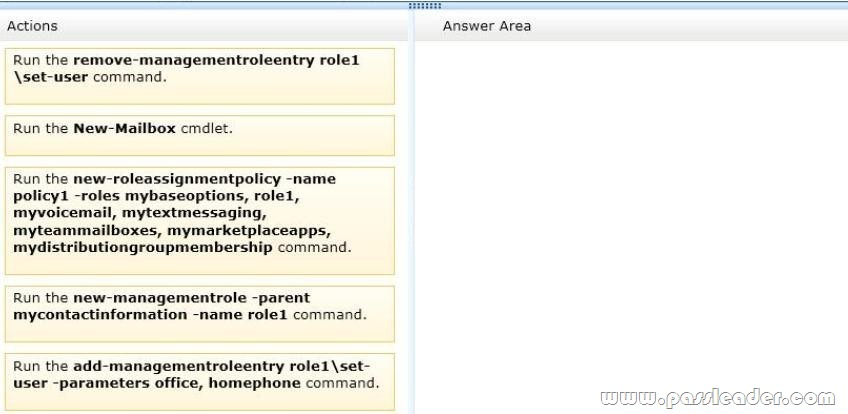
You create a new user account for a temporary user named User1. You plan to create a new mailbox for User1. You need to recommend which actions must be performed to ensure that User1 can modify only the values of his home phone number attribute and his office location attribute. In which order should you perform the actions? To answer, move all actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
QUESTION 85
Drag and Drop Question
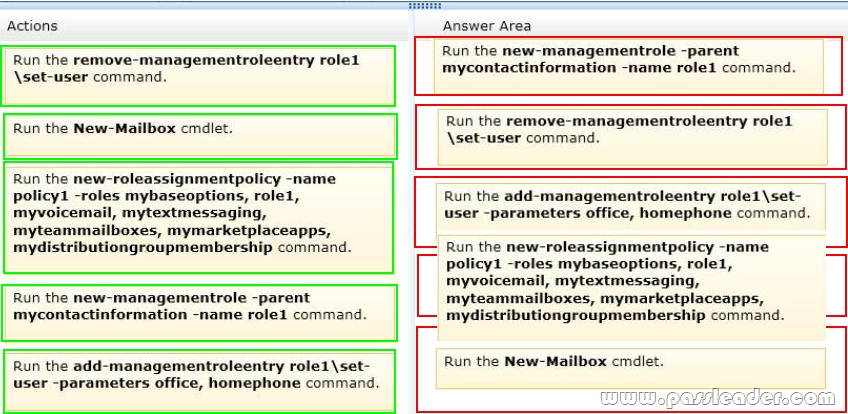
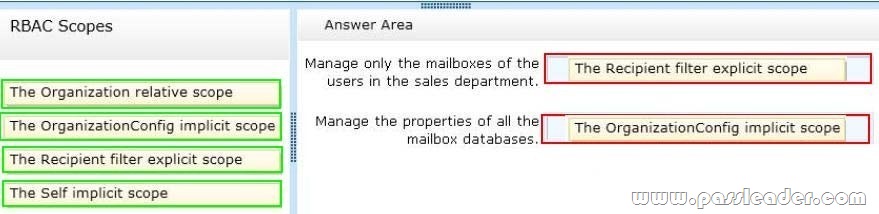
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains several custom RBAC management roles. You need to identify which RBAC scopes must be used to meet the following requirements:
– Manage only the mailboxes of the users in the sales department.
– Manage the properties of all the mailbox databases.
Which RBAC scopes should you identify? (To answer, drag the appropriate RBAC scopes to the correct requirements. Each RBAC scope may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)

Answer:
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd335146(v=exchg.150).aspx
Management role scopes enable you to define the specific scope of impact or influence of a management role when a management role assignment is created. When you apply a scope, the role assignee assigned to the role can only modify the objects contained within that scope. A role assignee can be a management role group, management role, management role assignment policy, user, or universal security group (USG). Every management role, whether it’s a built-in role or a custom role, has management scopes. Management scopes can be either of the following:
– Regular
A regular scope isn’t exclusive. It determines where, in Active Directory, objects can be viewed or modified by users assigned the management role. In general, a management role indicates what you can create or modify, and a management role scope indicates where you can create or modify. Regular scopes can be either implicit or explicit scopes, both of which are discussed later in this topic.
– Exclusive
An exclusive scope behaves almost the same as a regular scope. The key difference is that it enables you to deny users access to objects contained within the exclusive scope if those users aren’t assigned a role associated with the exclusive scope. All exclusive scopes are explicit scopes, which are discussed later in this topic.
Scopes can be inherited from the management role, specified as a predefined relative scope on a management role assignment, or created using custom filters and added to a management role assignment. Scopes inherited from management roles are called implicit scopes while predefined and custom scopes are called explicit scopes. Implicit scopes are the default scopes that apply to a management role type. Because implicit scopes are associated with a management role type, all of the parent and child management roles with the same role type also have the same implicit scopes. Implicit scopes apply to both built-in management roles and also to custom management roles. Implicit scopes defined on management roles.
Implicit scopes Description.
Organization If Organization is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can create or modify recipient objects across the Exchange organization. If Organization is present in the role’s recipient read scope, roles can view any recipient object across the Exchange organization. This scope is used only with recipient read and write scopes. MyGAL If MyGAL is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can view the properties of any recipient within the current user’s global address list (GAL). If MyGAL is present in the role’s recipient read scope, the role can view the properties of any recipient within the current GAL. This scope is used only with recipient read scopes. Self If Self is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can modify only the properties of the current user’s mailbox. If Self is present in the role’s recipient read scope, the role can view only the properties of the current user’s mailbox. This scope is used only with recipient read and write scopes.
MyDistributionGroups.
If MyDistributionGroups is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can create or modify distribution list objects owned by the current user. If MyDistributionGroups is present in the role’s recipient read scope, the role can view distribution list objects owned by the current user. This scope is used only with recipient read and write scopes.
OrganizationConfig.
If OrganizationConfig is present in the role’s configuration write scope, the role can create or modify any server or database configuration object across the Exchange organization. If OrganizationConfig is present in the role’s configuration read scope, the role can view any server or database configuration object across the Exchange organization. This scope is used only with configuration read and write scopes. None If None is in a scope, that scope isn’t available to the role. For example, a role that has None in the recipient write scope can’t modify recipient objects in the Exchange organization. Explicit scopes are scopes that you set yourself to control which objects a management role can modify. Although implicit scopes are defined on a management role, explicit scopes are defined on a management role assignment. This enables the implicit scopes to be applied consistently across all management roles unless you choose to use an overriding explicit scope. For more information about management role assignments, see Understanding Management Role Assignments. Explicit scopes override the implicit write and configuration scopes of a management role. They don’t override the implicit read scope of a management role. The implicit read scope continues to define what objects the management role can read.
Explicit scopes are useful when the implicit write scope of a management role doesn’t meet the needs of your business. You can add an explicit scope to include nearly anything you want as long as the new scope doesn’t exceed the bounds of the implicit read scope. The cmdlets that are part of a management role must be able to read information about the objects or containers that contain objects for the cmdlets to create or modify objects. For example, if the implicit read scope on a management role is set to Self, you can’t add an explicit write scope of Organization because the explicit write scope exceeds the bounds of the implicit read scope.
The OrganizationConfig implicit scope.
If OrganizationConfig is present in the role’s configuration write scope, the role can create or modify any server or database configuration object across the Exchange organization. If OrganizationConfig is present in the role’s configuration read scope, the role can view any server or database configuration object across the Exchange organization.
CAN MANAGE THE PROPERTIES OF ALL OF THE MAILBOX DATABASES
The Self Implicit Scope If Self is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can modify only the properties of the current user’s mailbox. If Self is present in the role’s recipient read scope, the role can view only the properties of the current user’s mailbox.
CANNOT BE SELF AS IT PERTAINS TO ONLY THE PARTICULAR USER’S MAILBOX
The Organization relative scope.
If Organization is present in the role’s recipient write scope, the role can create or modify recipient objects across the Exchange organization. If Organization is present in the role’s recipient read scope, roles can view any recipient object across the Exchange organization. This scope is used only with recipient read and write scopes.
NOT MEANT FOR MANAGING MAILBOX DATABASES
A recipient is any mail-enabled object in the Active Directory directory service to which Exchange can deliver or route messages. In Microsoft Exchange recipients are comprised of mailbox users, mail-enabled users, mail contacts, distribution groups, security groups, dynamic distribution groups, and mail-enabled public folders.
The Recipient filter explicit scope.
Recipient filter scopes use filters to target specific recipients based on recipient type or other recipient properties such as department, manager, location, and more.
CAN TARGET THE USERS IN THE SALES DEPARTMENT
QUESTION 86
Drag and Drop Question
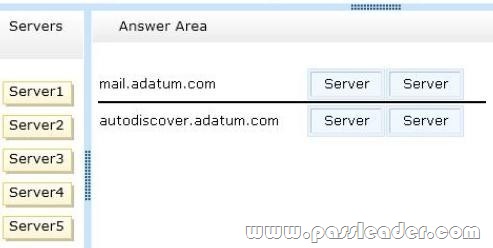
You have an Exchange Server 2007 organization. You are migrating the organization to Exchange Server 2013. The migration will last eight weeks. All servers are in a site named Site1. The servers in the organization are configured as shown in the following table. Users who have mailboxes on all of the servers will access Outlook Anywhere by using the mail.adatum.com name. You need to recommend which servers must be associated to the autodiscover.adatum.com and mail.adatum.com names. Which servers should you identify for each name? (To answer, drag the appropriate servers to the correct names. Each server may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Answer:

Explanation:
INCOMPLETE INFORMATION.
MAKES IT TOO DIFFICULT TO EVEN GUESS HOW TO ARRIVE AT THE CORRECT ANSWER MAY DEPEND ON THE TYPE OF SERVER (MAILBOX OR CLIENT ACCESS SERVER THAT IS IN USE OR THE VERSION OF OUTLOOK BEING USED. TO DETERMINE IF AUTODISCOVER CAN BE UTILISED ON THAT PARTICULAR SERVER. WHEN CAN YOU USE AUTODISCOVER WHEN CAN YOU NOT USE AUTODISCOVER.
Autodiscover.
Exchange Autodiscover is a service which is run on Exchange Client Access Servers. It is one of the new features it included in exchange 2007+ The Autodiscover service makes it easier to configure Outlook 2007 ,Outlook 2010 + and some mobile phones. Autodiscover Service cannot be used with earlier versions of Outlook, including Outlook 2003. In earlier versions of Microsoft Exchange (Exchange 2003 SP2 or earlier) and Outlook (Outlook 2003 or earlier), you had to configure all user profiles manually to access Exchange. The Autodiscover service uses a user’s e-mail address and password to automatically configure a user’s profile. Using the e-mail address, the Autodiscover service provides the following information to the client:
– The user’s display name.
– Separate connection settings for internal and external connectivity.
– The location of the user’s Mailbox server.
– The URLs for various Outlook features that manage functionality such as OOF, free/busy information, Unified Messaging, and the offline address book.
– Outlook Anywhere server settings.
Additionally, a new Active Directory object named the service connection point (SCP) is created on the server where you install the Client Access server role. And Autodiscover information is stored in it. Exchange 2013 requires its Outlook clients support auto-discovery of the server; this is in part to help streamline cloud deployments of Exchange. Clients also have to support “Outlook Anywhere” access–remote procedure calls via HTTP–to connect to Exchange 2013 instead of using TCP-based RPCs as in older versions of Exchange. What actually happens after you have entered your details is that the client looks for autodiscover.yourdomain.com and attempts to retrieve the rest of the server configuration details from there.
QUESTION 87
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. All user mailboxes have an In-Place Archive enabled. You need to identify which email message types can be archived by using a retention policy. Which message type or types should you identify? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose all that apply.)
A. calendar items
B. mail items
C. note items
D. task items
E. contact items
Answer: BCE
QUESTION 88
Your company, Fabrikam Inc., has an Exchange Server 2013 organization. The organization that contains three servers named Server1, Server2, and Server3. Server1 and Server2 are members of a database availability group (DAG) named DAG1. DAG1 contains two mailbox databases. All databases are active on Server1 and replicate to Server2. You start an unplanned maintenance on Server1 and shut down Server1. You discover that the databases do not mount on Server2. You restart Server1 and the databases mount automatically on Server1. You need to identify what prevents the databases from switching over successfully to Server2. Which cmdlet should you run?
A. Test-ReplicationHealth
B. Test-OutlookConnectivity
C. Test-ServiceHealth
D. Get-AvailabilityReportOutage
Answer: A
Explanation:
The cmdlet is designed for the proactive monitoring of continuous replication and the continuous replication pipeline, the availability of Active Manager, and the health and status of the underlying cluster service, quorum, and network components. The Test-ReplicationHealth cmdlet can be run locally or remotely against any Mailbox server in a DAG.
NOT B
Test-OutlookConnectivity.
Use the Test-OutlookConnectivity cmdlet to test end-to-end Microsoft Outlook client connectivity in the Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 organization. This includes testing for Outlook Anywhere (RPC/HTTP) connections.
EXAMPLE 1
This example runs a protocol test from the Mailbox server.
Test-OutlookConnectivity -ProbeIdentity “OutlookSelfTestProbe”
NOT C
Use the Test-ServiceHealth cmdlet to test whether all the Microsoft Windows services that Exchange requires on a server have started. The Test-ServiceHealth cmdlet returns an error for any service required by a configured role when the service is set to start automatically and isn’t currently running.
EXAMPLE 1
This example uses the Test-ServiceHealth command without parameters to test the services on the local server.
Test-ServiceHealth
NOT D
Use the Get-AvailabilityReportOutage cmdlet to return the daily downtime (if any) for each service entity and its overridden value (if set) to the overall reported availability for the day. For information about the parameter sets in the Syntax section below, see Syntax. This example returns all outages that occurred the previous day. This cmdlet always returns outages for one day.
Get-AvailabilityReportOutage
QUESTION 89
You have an Exchange Server 2010 organization named adatum.com. You deploy a server that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. You plan to install eight additional servers that have Exchange Server 2013 installed. You are a member of the Organization Management management role group. You hire a temporary Exchange administrator named Temp1. The company’s security policy states that all external consultants must have the minimum number of required permissions on the network. You need to ensure that Temp1 can install a server named Server5. The solution must meet the requirements of the security policy. Which two tasks should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Run setup and specify the /newprovisionedserver:Server5 parameter.
B. Add Temp1 to the Delegated Setup management role group.
C. Add Temp1 to the Exchange Server role group.
D. Create a new management role and a new role assignment policy.
E. Run setup and specify the /roles:temp1 parameter.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
NOT C
Unable to install a server given this management role. The Exchange Servers management role enables administrators to do the following on individual servers:
– Add and remove database availability groups and configure database copies
– Enable, disable and configure Unified Messaging services
– Modify transport configuration on Mailbox and Client Access servers
– Enable and disable Microsoft Outlook Anywhere on Client Access servers
– Modify Mailbox and Client Access server configuration
– Modify Outlook Anywhere configuration on Client Access servers
– Modify content filtering configuration on Mailbox servers
– Modify general Exchange server configuration
– Modify server monitoring configuration
– View the configuration for each server role
This management role is one of several built-in roles in the Role Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions model in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. Management roles, which are assigned to one or more management role groups, management role assignment policies, users, or universal security groups (USG), act as a logical grouping of cmdlets or scripts that are combined to provide access to view or modify the configuration of Exchange 2013 components, such as mailbox databases, transport rules, and recipients. If a cmdlet or script and its parameters, together called a management role entry, are included on a role, that cmdlet or script and its parameters can be run by those assigned the role. For more information about management roles and management role entries, see Understanding Management Roles.
NOT D
No need to create a new management role.
NOT E
Need to use the /NewProvisionedServer parameter setup /roles command is OK for exchange 2007. With temp1 appears to be an invalid command and not applicable to exchange 2013.
A
To delegate setup, you must first run Setup.com from a Command Prompt window with the /NewProvisionedServer parameter. This will not install Exchange on the server, but instead will create a placeholder object for the server in Active Directory and will add the machine account for this server to the Exchange Servers group.
B
Need to Add Temp1 to the Delegated Setup management role group.
Delegated Setup management role group.
The Delegated Setup management role group is one of several built-in role groups that make up the Role Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions model in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. Role groups are assigned one or more management roles that contain the permissions required to perform a given set of tasks. The members of a role group are granted access to the management roles assigned to the role group. For more information about role groups, see Understanding Management Role Groups. Administrators who are members of the Delegated Setup role group can deploy servers running Exchange 2013 that have been previously provisioned by a member of the Organization Management role group. Members of the Delegated Setup role group can only deploy Exchange 2013 servers. They can’t manage the server after it’s been deployed. To manage a server after it’s been deployed, a user must be a member of the Server Management role group. For more information about RBAC, see Understanding Role Based Access Control.
QUESTION 90
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two Client Access servers named EX1 and EX2 and two Mailbox servers named EX3 and EX4. You have a firewall that controls all of the traffic between the internal network and the Internet. EX3 and EX4 are prevented from communicating with Internet hosts. EX1 and EX3 are in a site named Site1. EX2 and EX4 are in a site named Site2. All outbound email is sent through EX1. Site1 fails. You discover that email messages for the Internet are queued on EX4. You create a new send connector in Site2. You discover that all of the outbound email is queued on EX4 and is not delivered to the Internet. You verify that the client computers on the network can receive email messages from the Internet successfully. You need to ensure that the email messages are delivered successfully to the Internet. Which cmdlet should you run?
A. Set-SendConnector
B. Set-MailboxTransportService
C. Set-TransportService
D. Set-TransportServer
Answer: A
QUESTION 91
Drag and Drop Question
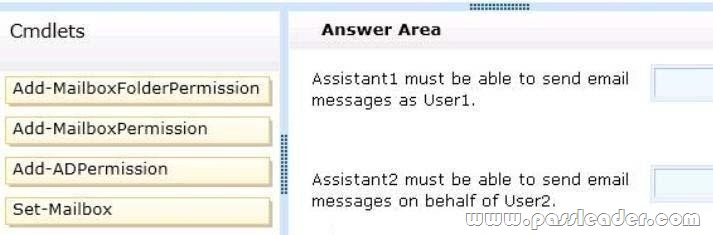
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains a server named Server1. A user named User1 has an administrative assistant named Assistant1. A user named User2 has an administrative assistant named Assistant2. You need to configure access to Outlook to meet the following requirements:
– Assistant1 must be able to send email messages as a User1.
– Assistant2 must be able to send email messages on behalf of User2.
Which cmdlets should you use? (To answer, drag the appropriate cmdlets to the correct requirements. Each cmdlet may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Answer:
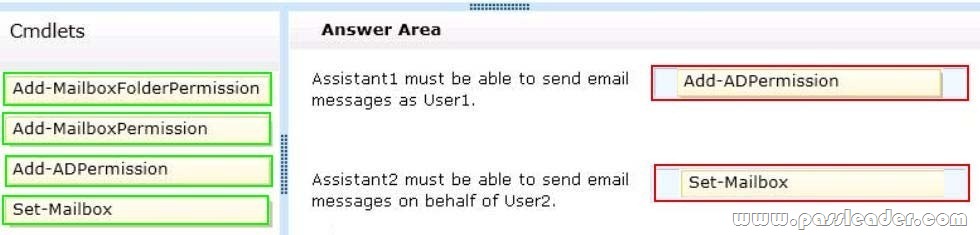
Explanation:
Add-MailboxFolderPermission.
Use the Add-MailboxFolderPermission cmdlet to manage folder-level permissions for all folders within a user’s mailbox. For information about the parameter sets in the Syntax section below, see Syntax. This example assigns permissions for Ed to access Ayla’s Marketing mailbox folder and applies the Owner role to his access of that folder.
Add-MailboxFolderPermission -Identity [email protected]:\Marketing -User
[email protected] ?AccessRights Owner
Add-MailboxPermission
Use the Add-MailboxPermission cmdlet to add permissions to a mailbox. This example grants Kevin Kelly full access to Terry Adams’s mailbox.
Note:
The Identity parameter requires the full name of the user to be enclosed in quotation marks (“). Add-MailboxPermission -Identity “Terry Adams” -User KevinKelly -AccessRights
FullAccess ?InheritanceType
All
Add-ADPermission.
Use the Add-ADPermission cmdlet to add permissions to an Active Directory object. This example grants Send As permissions for Aaron Painter to Terry Adams’s mailbox.
Add-ADPermission -Identity “Terry Adams” -User AaronPainter -AccessRights ExtendedRight -ExtendedRights
“Send As” Send As rights is applied to Active directory object.
Set-Mailbox.
Use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet to modify the settings of an existing mailbox. You can use this cmdlet for one mailbox at a time. To perform bulk management, you can pipeline the output of various Get-cmdlets (for example, the Get-Mailbox or Get-User cmdlets) and configure several mailboxes in a single-line command. You can also use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet in scripts. For information about the parameter sets in the Syntax section below, see Syntax. This example delivers John Woods’s email messages to John’s mailbox and also forwards them to Manuel Oliveira’s ([email protected]) mailbox.
Set-Mailbox -Identity John -DeliverToMailboxAndForward $true -ForwardingSMTPAddress [email protected]
Send on Behalf.
The Send on Behalf permission allows a user to send email on behalf of the shared mailbox. For example, if John logs into the shared mailbox Reception Building 32 and sends an email, it will appear to recipients as being sent by “John on behalf of Reception Building 32”. To grant Send on Behalf permissions, you must use the Exchange Management Shell. Use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet with the GrantSendonBehalf parameter.
QUESTION 92
Hotspot Question
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains 10 mailbox servers. You have a custom workload management policy named App1Policy. App1Policy is applied to three Mailbox servers. You deploy a new Mailbox server named EX11. You need to ensure that App1Policy is applied to EX11. Which command should you run? (To answer, configure the appropriate options in the answer area.)
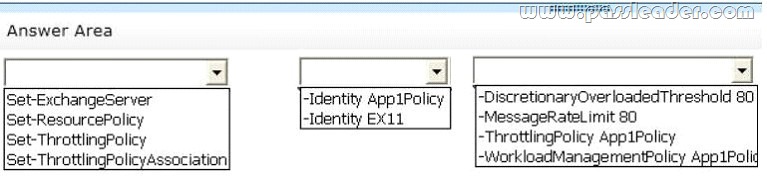
Answer:

Explanation:
An Exchange workload is an Exchange Server feature, protocol, or service that’s been explicitly defined for the purposes of Exchange system resource management. Each Exchange workload consumes system resources such as CPU, mailbox database operations, or Active Directory requests to run user requests or background work. Examples of Exchange workloads include Outlook Web App, Exchange ActiveSync, mailbox migration, and mailbox assistants. There are two ways to manage Exchange workloads: by monitoring the health of system resources or by controlling how resources are consumed by individual users (sometimes called user throttling in Exchange 2010). Managing workloads based on the health of system resources is new in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. Controlling how resources are consumed by individual users was possible in Exchange Server 2010, and this capability has been expanded for Exchange Server 2013. You can customize the workload management settings if you want to change the default behavior of the feature for the needs of your environment.
SECTION1
Use the Set-ExchangeServer cmdlet to set Exchange attributes in Active Directory for a specified server.
(EX11)
Not a throttling policy. Scenario details a workload management policy. Use the Set-ResourcePolicy cmdlet to set the properties of a custom resource policy.
SECTION2
The Identity parameter specifies the GUID, distinguished name (DN), or name of the server. Need EX11 as it is the name of the server.
SECTION3
The WorkloadManagementPolicy parameter specifies the name of a workload management policy to apply in Active Directory. (App1Policy) Not a throttling policy.
QUESTION 93
Hotspot Question
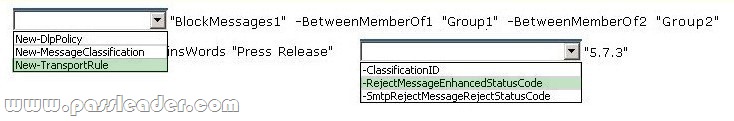
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two distribution groups named Groupl and Group2. You need to prevent the members of Groupl and Group2 from communicating with each other by using email, unless the email messages contain the string Press Release in the subject. Users whose email messages are rejected must receive a non-delivery report (NDR) that contains a status code of 5.7.3. Which command should you run? (To answer, configure the appropriate options in the answer area.)

QUESTION 94
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named for A.Datum Inc. A user named User1 is a member of the Domain Admins group. User1 fails to synchronize a new Windows Phone device by using Exchange ActiveSync and receives an HTTP 500 error message. User1 successfully logs on to Outlook Web App and Outlook Anywhere. You need to ensure that User1 can synchronize the new Windows Phone device by using Exchange ActiveSync. Which two tasks should you perform? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose two.)
A. Disable permission inheritance on the User1 user account.
B. Enable permission inheritance on the User1 user account.
C. Install a trusted root certificate on the Windows Phone device.
D. Create a new mobile device mailbox policy.
E. Modify the Exchange ActiveSync policy that applies to User1’s mailbox.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
HTTP 500 ERROR MESSAGE.
The Web server (running the Web Site) encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request by the client (e.g. your Web browser or our CheckUpDown robot) for access to the requested URL.
B
Simply check include inheritable permissions from this object’s parent.
INHERITABLE PERMISSIONS
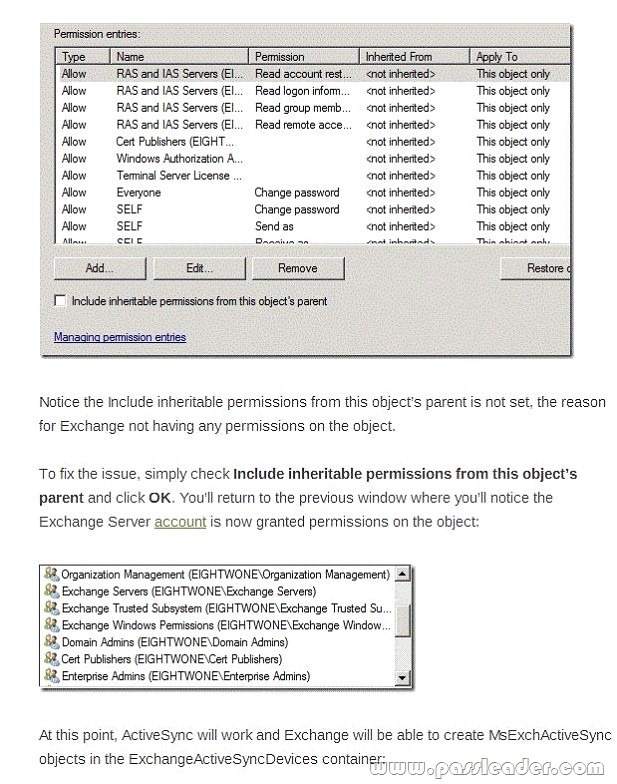
NOT A
Need to enable permission inheritance on the User1 user account not disable it.
NOT C
This solution will fix a different error. (Error 80072F0D) error. This error can occur when the root certificate authority that generated the SSL certificate being used by the Exchange server is not trusted by the Windows Phone device. This will commonly occur with Exchange servers that are still configured to use a self-signed certificate, or that have a certificate issued from a private CA.
NOT D
No need to create a new policy but need to modify the existing policy.
E
It appears that Exchange ActiveSync for User 1’s mailbox may not be enabled. Use the EAC to enable or disable Exchange ActiveSync:
– In the EAC, navigate to Recipients > Mailboxes.
– In the list of user mailboxes, click the mailbox that you want to enable or disable Exchange ActiveSync for, and then click Edit.
– On the mailbox properties page, click Mailbox Features.
– Under Mobile Devices, do one of the following:
* To disable Exchange ActiveSync click Disable Exchange ActiveSync. A warning appears asking if you’re sure you want to disable Exchange ActiveSync. Click Yes.
* To enable Exchange ActiveSync, click Enable Exchange ActiveSync. Click Save to save your change.
Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policies control how users use and synchronize their mobile devices in your organization. When you change an Exchange ActiveSync device policy, it affects all users whose mailbox is associated with that policy. The policy you set as the default automatically affects all users in the organization except those you have explicitly assigned different device policies to. Not all mobile devices support all the Exchange ActiveSync policy settings. If a policy setting isn’t supported on a particular device, the device may not apply the setting. You can control whether devices that don’t support specific policies are allowed to connect in the General settings for the policy.
QUESTION 95
Your company has a main office and a branch office. You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. The company recently built a new meeting room in the branch office. You need to ensure that the meeting room is available by using the Room Finder feature in Microsoft Outlook. Which cmdlet should you run?
A. Set-MailboxCalendarConfiguration
B. New-Mailbox
C. Set-CalendarProcessing
D. New RemoteMailbox
Answer: B
Explanation:
New-Mailbox.
Create a new Room Mailbox to schedule meetings in conference rooms, auditoriums, labs or other facilities: New-Mailbox -Name <Room Name> -Room

NOT A
Use the New-RemoteMailbox cmdlet to create a mail-enabled user in the on-premises Active Directory and also create an associated mailbox in the cloud-based service. Not designed for room mailboxes.
NOT C
Use the Set-MailboxCalendarConfiguration cmdlet to apply calendar settings for users using Microsoft Office Outlook Web App calendars.
NOT D
Use the Set-CalendarProcessing cmdlet to modify calendar-related processing configuration properties for the target mailbox, which include Calendar Attendant, resource booking assistant, and calendar configuration.
B
New-Mailbox.
Create a new Room Mailbox to schedule meetings in conference rooms, auditoriums, labs or other facilities Create new Room Mailbox PowerShell command syntax:
New-Mailbox -Name <Room Name> -Room
Example:
New-MailBox -Name FL-ROOM1 -Room
A Look at Exchange Server 2013 Resource Mailboxes.
http://exchangeserverpro.com/exchange-server-2013-room-equipment-mailboxes/
Resource mailboxes have been around for a few versions of Exchange Server, and Exchange Server 2013 brings us a few improvements in how they are managed. There are two types of resource mailboxes:
Room mailboxes are for fixed locations such as meeting rooms or conference facilities Equipment mailboxes are for items that are not fixed to a location, such as laptops or vehicles Exchange 2013 puts resource mailboxes under their own section of the Exchange Administration Center. Both room and equipment mailboxes are managed in this same section.
One of the immediate improvements is that you are able to set the booking policy or assign delegates during the creation of the resource mailbox, rather than as a secondary task after the mailbox is created.
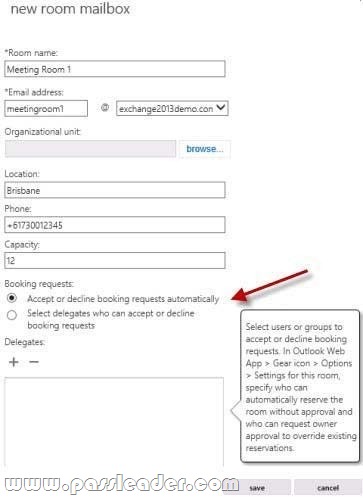
After the mailbox has been created there are a few additional properties you can customize. The booking options can be further tuned with regards to recurring meetings, booking horizon, and custom replies.

You can also easily configure a MailTip for the resource mailbox.

The text that you place in the MailTip will appear automatically when people add the room or resource mailbox to a meeting request in Outlook. Although in my opinion the MailTip needs some color to draw the person’s attention to it.

Finally, an interesting default setting is the disabling of email address policies. This does make sense as most resource mailboxes are for internal use only, so having email address policies assigning multiple SMTP addresses to resource mailboxes is usually not necessary.

Overall it appears that room and resource mailboxes are a feature that has matured over the previous versions of Exchange Server and now receive just a few minor improvements to make them simpler to manage.
QUESTION 96
Drag and Drop Question
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains five servers. Several employees plan to use Microsoft Outlook to collaborate on some projects. You need to configure access to Outlook to meet the following requirements:
– Several employees must be able to open only the Inbox of a user named Userl.
– Several employees must be able to copy email messages from any folder in the mailbox of a user named User2.
– Several employees must be able to create only contacts in the mailbox of a user named User3.
Which cmdlets should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate cmdlet to the correct requirement in the answer area. Each cmdlet may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Additionally, you may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.

Answer:

Explanation:
Add-MailboxFolderPermission.
Use the Add-MailboxFolderPermission cmdlet to manage folder-level permissions for all folders within a user’s mailbox.
EXAMPLE 1
This example assigns permissions for Ed to access Ayla’s Marketing mailbox folder and applies the Owner role to his access of that folder.
Add-MailboxFolderPermission -Identity [email protected]:\Marketing -User
[email protected] ?AccessRights Owner
Add-MailboxPermission
Use the Add-MailboxPermission cmdlet to add permissions to a mailbox.
EXAMPLE 1
This example grants Kevin Kelly full access to Terry Adams’s mailbox.
Note:
The Identity parameter requires the full name of the user to be enclosed in quotation marks (“). Add-MailboxPermission -Identity “Terry Adams” -User KevinKelly -AccessRights
FullAccess ?InheritanceType
All
Set-Mailbox.
Use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet to modify the settings of an existing mailbox. You can use this cmdlet for one mailbox at a time. To perform bulk management, you can pipeline the output of various Get- cmdlets (for example, the Get-Mailbox or Get-User cmdlets) and configure several mailboxes in a single-line command. You can also use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet in scripts.
EXAMPLE 1
This example delivers John Woods’s email messages to John’s mailbox and also forwards them to Manuel Oliveira’s ([email protected]) mailbox.
Set-Mailbox -Identity John -DeliverToMailboxAndForward $true -ForwardingSMTPAddress [email protected]
STEPS
1. Use the Add-MailboxFolderPermission cmdlet to manage folder-level permissions for all folders within a user’s mailbox.
2. Use the Add-MailboxPermission cmdlet to add permissions to a mailbox.
3. Use the Add-MailboxFolderPermission cmdlet to manage folder-level permissions for all folders within a user’s mailbox.
QUESTION 97
Hotspot Question
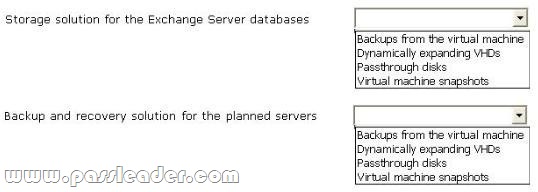
You are planning to implement several servers on virtual machines. The servers have Exchange Server 2013 installed. The planned implementation must meet the following requirements:
– Minimize the amount of overhead required for the virtualization solution.
– Minimize the risk of data corruption for the Exchange Server databases.
You need to recommend a storage solution for the Exchange databases and a backup and recovery solution for the planned servers. Which solutions should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate solutions in the answer area.
QUESTION 98
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain named contoso.com. You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named Contoso. You plan to create an additional SMTP domain named sales.contoso.com. You will use sales.contoso.com as the primary SMTP address for the users in the sales department. You create a new email address policy and apply the policy to the sales users. New sales users report that when they attempt to access their email from the Internet for the first time by using Microsoft Outlook 2010, they fail to connect. The sales users connect to their mailbox internally successfully by using Outlook 2010. All other users can connect to their mailbox from the Internet and internally. You need to ensure that the new sales users can connect to the Exchange Server 2013 organization by using Outlook Anywhere from the Internet. Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Modify each existing Service Connection Point (5CP) object in Active Directory to point to auto discover.sales.contoso.com.
B. From DNS Manager, create a host (A) record for autodiscover.sales.contoso.com.
C. On the Client Access servers, deploy a new certificate that includes the autodiscover.sales.contoso.com name.
D. Create a new Autodiscover virtual directory on the Client Access servers and configure ExternalURL to use autodiscover.sales.contoso.com.
E. Create a new Service Connection Point (SCP) object in Active Directory that points to auto discover.sales.contoso.com.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
– Externally connected clients are different, because they can’t lookup the SCP in Active Directory from outside of the network. These clients might be roaming laptop users with Outlook, or they might be ActiveSync capable smartphones such as iPhones. In either case they will attempt to connect to Autodiscover by performing a DNS lookup for “autodiscover.smtpdomainname”.
– You need the “autodiscover.smtpdomainname” name in the Exchange 2013 SSL certificate. (C)
– You will only need an autodiscover name for each SMTP domain that a user is likely to enter as their email address. (B)
QUESTION 99
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named Contoso. The organization contains a server named Server1 that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. Server1 has the Mailbox server role and the Client Access server role installed. Server1 has a Send connector for a partner company. The Send connector is configured for Domain Security with a domain named adatum.com. The only certificate installed on Server1 expires. You discover that all email messages sent to adatum.com remain in the queue on Server1. On Server1, you install a new certificate from a trusted third-party. You need to ensure that the email messages are delivered to adatum.com. What should you do?
A. Assign the new certificate to the IIS service.
B. Send the new certificate to the administrator at adatum.com.
C. Assign the new certificate to the SMTP service.
D. Create a new send connector that contains an address space to adatum.com.
Answer: C
Explanation:
– The Enable-ExchangeCertificate cmdlet enables certificates when it updates the metadata that is stored with the certificate. To enable an existing certificate to work with different services, run the Enable-ExchangeCertificate command and specify the services that you want to enable.
– You can rerun this cmdlet if you want to add new services that use the certificate. When you enable a certificate for the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) service and the certificate contains a FQDN that matches the FQDN of the local computer, the certificate may be published to the Active Directory directory service.
QUESTION 100
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains an enterprise root certification authority (CA) named CA1. The network contains a server named EX1 that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. A partner company named A . Datum Corporation has an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains a server named EX5 that has Exchange Server 2010 Service Pack 2 (SP2) installed. EX5 has a Receive connector that is configured for mutual TLS. Users in contoso.com plan to send email messages that contain sensitive data to users in adatum.com. You need to ensure that all of the email messages sent from contoso.com to adatum.com are encrypted by using TLS. The solution must ensure that EX1 and EX5 validate server certificates. Which three actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)
A. Run the set-transportconfig -tlssenddomainsecurelist contoso.com command.
B. Install a certificate, and then assign the certificate to the IIS service.
Send the root certificate for contoso.com to the administrators in adatum.com.
C. Run the New-SendConnector cmdlet and specify the domainsecureenabled parameter.
D. Run the New-SendConnector cmdlet and specify the tlsdomainparameter.
E. Run the set-transportconfig -tlssenddomainsecurelist adatum.com command.
F. Install a certificate, and then assign the certificate to the SMTP service.
Send the root certificate for contoso.com to the administrators in adatum.com.
Answer: ADF
Explanation:
A: Use the Set-TransportConfig cmdlet to modify the transport configuration settings for the whole Exchange organization. TheTLSSendDomainSecureListparameter specifies the domains from which you want to send domain secured email by using mutual TLS authentication. In this scenario we send from EX1 in the contoso.com domain.
D: Need to create a new send connector. The TlsDomain parameter specifies the domain name that the Send connector uses to verify the FQDN of the target certificate when establishing a TLS secured connection.
F: A new certificate is needed for the SMTP service.
Get the newest PassLeader 70-341 VCE dumps here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 70-341 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM