Valid 98-366 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 98-366 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 98-366 VCE dumps and 98-366 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 98-366 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 98-366 dumps with VCE and PDF here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 98-366 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc
QUESTION 21
In which physical network topology is each computer connected to a central point?
A. Star
B. Mesh
C. Ring
D. Bus
Answer: A
Explanation:
In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
QUESTION 22
Which two of the following are connectivity options for wide area networks (WANs)? (Choose two.)
A. Token ring
B. Ethernet
C. Dial-up
D. Leased line
Answer: CD
Explanation:
Token ring and Ethernet are used in LANs.
QUESTION 23
A private network that allows members of an organization to exchange data is an ____.
A. Extranet
B. Ethernet
C. Intranet
D. Internet
Answer: C
Explanation:
An intranet is a computer network that uses Internet Protocol technology to share information, operational systems, or computing services within an organization. This term is used in contrast to extranet, a network between organizations, and instead refers to a network within an organization.
QUESTION 24
Security is a concern on wireless networks due to ____.
A. the radio broadcast access method
B. spread spectrum issues
C. frequency modulation issues
D. the potential for cross-talk
Answer: A
QUESTION 25
A characteristic of the mesh topology is that it ____.
A. uses a central hub
B. cannot use wired connections
C. uses redundant paths
D. cannot use wireless connections
Answer: C
Explanation:
Mesh network topology is one of the key network architectures in which devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes such as routers and switches. In a mesh topology, if any cable or node fails, there are many other ways for two nodes to communicate.
QUESTION 26
To protect a network when it is connected to the Internet, you should use a ____.
A. Bridge
B. Firewall
C. Switch
D. Router
Answer: B
Explanation:
A firewall is software or hardware that checks information coming from the Internet or a network, and then either blocks it or allows it to pass through to your computer, depending on your firewall settings.
QUESTION 27
One purpose of a perimeter network is to ____.
A. make resources available to the intranet
B. link campus area networks (CANs)
C. link local area networks (LANs)
D. make resources available to the Internet
Answer: D
Explanation:
In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to a larger and untrusted network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN); an external network node only has direct access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network.
QUESTION 28
Which protocol can be used to encrypt packets on the Internet?
A. SNMP
B. HTTPS
C. TFTP
D. HTTP
Answer: B
Explanation:
HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, makes it more difficult for hackers, the NSA, and others to track users. The protocol makes sure the data isn’t being transmitted in plain-text format, which is much easier to eavesdrop on.
QUESTION 29
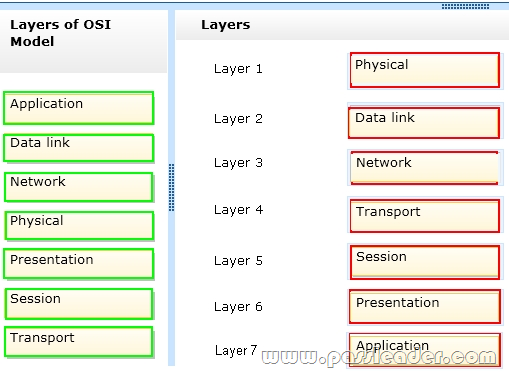
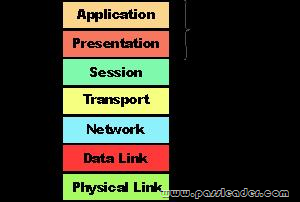
Drag and Drop
Order the layers of the OSI model:
QUESTION 30
The service that resolves fully qualified domain names (FQDN) to IP addresses is ____.
A. Windows Internet Name Service (WINS).
B. Domain Name Service (DNS).
C. Internet Service Provider (ISP).
D. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Answer: B
Explanation:
The DNS translates Internet domain and host names to IP addresses. DNS automatically converts the names we type in our Web browser address bar to the IP addresses of Web servers hosting those sites.
QUESTION 31
If a router is installed so that it separates a DHCP server from its clients, the clients will ____.
A. immediately lose connectivity to all segments
B. be unable to obtain their leases from the server
C. immediately lose connectivity to the local segment
D. receive an immediate renewal of their lease
Answer: B
QUESTION 32
Which of the following services masks internal IP addresses from outside the network?
A. DHCP
B. WINS
C. NAT
D. DNS
Answer: C
Explanation:
The majority of NATs map multiple private hosts to one publicly exposed IP address. In a typical configuration, a local network uses one of the designated “private” IP address subnets (RFC 1918). A router on that network has a private address in that address space. The router is also connected to the Internet with a “public” address assigned by an Internet service provider.
QUESTION 33
The query protocol used to locate resources on a network is ____.
A. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
B. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
C. Tracert
D. Telnet
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network.
QUESTION 34
Tracert is used to ____.
A. manage routing tables dynamically
B. manage session-oriented connections between nodes
C. report the route taken by packets across an IP network
D. report the shortest route between different networks
Answer: C
Explanation:
In computing, traceroute (treacert) is a computer network diagnostic tool for displaying the route (path) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
QUESTION 35
In which OSI layer does routing occur?
A. Transport
B. Network
C. Data Link
D. Physical
Answer: B
Explanation:
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the network layer is layer 3. The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers.
QUESTION 36
What type of record does DNS use to find a mail service?
A. Service (SRV) DNS record
B. Canonical (CNAME) DNS record
C. Mail Exchanger (MX) DNS record
D. Host (A) DNS record
Answer: C
Explanation:
A mail exchanger record (MX record) is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System that specifies a mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a recipient’s domain, and a preference value used to prioritize mail delivery if multiple mail servers are available. The set of MX records of a domain name specifies how email should be routed with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
QUESTION 37
The default gateway address identifies the ____.
A. device that will connect the computer to the local network
B. device that will connect the computer to a remote network
C. server that will provide name services for the computer
D. server that will authenticate the user of the computer
Answer: B
Explanation:
A default gateway is the node on the computer network that the network software uses when an IP address does not match any other routes in the routing table. In home computing configurations, an ISP often provides a physical device which both connects local hardware to the Internet and serves as a gateway.
QUESTION 38
How many bits are there in an Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address?
A. 32
B. 64
C. 128
D. 256
Answer: C
Explanation:
IPv6 uses a 128-bit address, allowing 2128, or approximately 3.4×1038 addresses, or more than 7.9×1028 times as many as IPv4, which uses 32-bit addresses.
QUESTION 39
Which of the following is a public IP address?
A. 10.156.89.1
B. 68.24.78.221
C. 172.16.152.48
D. 192.168.25.101
Answer: B
Explanation:
The private address space specified in RFC 1918 is defined by the following three address blocks:
– Not D: 192.168.0.0/16
The 192.168.0.0/16 private network can be interpreted either as a block of 256 class C network IDs or as a 16-bit assignable address space (16 host bits) that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization. The 192.168.0.0/16 private network allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254.
– Not A: 10.0.0.0/8
The 10.0.0.0/8 private network is a class A network ID that allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 10.0.0.1 to 10.255.255.254. The 10.0.0.0/8 private network has 24 host bits that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization.
– Not C: 172.16.0.0/12
The 172.16.0.0/12 private network can be interpreted either as a block of 16 class B network IDs or as a 20-bit assignable address space (20 host bits) that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization. The 172.16.0.0/12 private network allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 172.16.0.1 to 172.31.255.254.
QUESTION 40
What is the minimum cabling requirement for a 100BaseTX network?
A. Category 3 UTP cable
B. Category 5 UTP cable
C. Category 6 UTP cable
D. Multimode fiber cable
Answer: B
Explanation:
100BASE-TX is the predominant form of Fast Ethernet, and runs over two wire-pairs inside a category 5 or above cable. 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T were both designed to require a minimum of Category 5 cable and also specify a maximum cable length of 100 meters. Category 5 cable has since been deprecated and new installations use Category 5e.
Get the newest PassLeader 98-366 VCE dumps here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 98-366 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc